Scope of Future Industrialization in Himachal Pradesh: Complete Notes
Executive Summary
Himachal Pradesh is positioned to become a major industrial hub in North India, with the state achieving remarkable 6.7% GSDP growth in 2024-25 and the secondary sector growing at 8.1%. The state’s future industrialization scope is particularly strong in pharmaceuticals (contributing 35% of India’s pharmaceutical production), renewable energy, food processing, and emerging sectors like biotechnology and information technology.hpgeneralstudies+3
Current Industrial Landscape
Economic Performance
- GSDP Growth: 6.7% in 2024-25, with per capita income increasing by 9.6% to ₹2,57,212hpgeneralstudies+1
- Sectoral Contribution: Secondary sector contributes 39.5% to GVA, tertiary sector 45.3%, and primary sector 15.2%medicalbuyer
- Industrial Growth: Secondary sector expected to grow at 8.1% in 2024-25, higher than the national average of 6.5%indiafilings
Established Industrial Base
The state has developed strong industrial corridors in Baddi-Barotiwala-Nalagarh, Paonta Sahib, Kala Amb, and Solan, hosting over 300 pharmaceutical manufacturing units and major industrial houses including ACC, Gujarat Ambuja Cement, Birla, Dabur, Cipla, and Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories.economictimes+1

Sector-wise growth potential assessment for future industrialization in Himachal Pradesh based on current market trends, government policies, and resource availability
Major Growth Sectors
1. Pharmaceutical Industry
Current Status: Leading contributor with 35% of India’s pharmaceutical productionmanufacturing.economictimes.indiatimes+1
- Annual Growth Rate: 8-10% with market value exceeding ₹30,000 crorephdcci
- Manufacturing Units: Over 300 pharmaceutical units, 25 contract manufacturing facilitiesmanufacturing.economictimes.indiatimes
- Export Contribution: 60% of state’s total exportshimachalservices
- Employment: Significant job creation in Baddi-Barotiwala belthpgeneralstudies
Future Prospects:
- First Medical Devices Park in North India established in Nalagarh with 265 acresmanufacturing.economictimes.indiatimes
- Growing biotechnology integration for drug development
- Expansion into biosimilar drugs and active pharmaceutical ingredients
2. Hydropower and Renewable Energy
Current Potential: 27,436 MW hydroelectric potential, with 10,519 MW already harnessedprojectstoday+1
- Ongoing Projects: Multiple projects including 450 MW Shongtong and 130 MW Kashang projectsprsindia
- World Bank Support: $200 million project for renewable energy expansionindianjournalofeconomicsandresearch
- Green Energy Target: Aiming to become India’s first Green Energy State by 2026himachalservices+1
Future Development:
- 626 MW solar projects under developmenthimachalpradesh.pscnotes+1
- Pump storage projects: Renukaji (1,630 MW) and multiple others totaling over 20,000 MW
- Green hydrogen production facilities in partnership with Oil India Limitedhimachalservices
3. Food Processing Industry
Recognition: Winner of “Best State in Food Processing Award-2024”cleartax
- Infrastructure: 23 food parks, 1 mega food park, 18 cold chain projectscleartax
- Investment Schemes: State Mission on Food Processing and Pradhan Mantri Kisan Sampada Yojanahpgeneralstudies+1
- Sanctioned Units: 1,320 micro food processing enterprises approvedcleartax
Growth Areas:
- Apple processing and value addition (state produces 90% of India’s apples)
- Organic food processing leveraging natural farming initiatives
- Fruit juice, jam, and preserved food manufacturing
- Dairy processing and cold chain development
4. Information Technology
Current Initiatives: IT Policy focusing on Shimla and Dharamshala as IT hubsemerginghimachal.hp
- Digital Infrastructure: Online application systems for business approvals
- Government Support: Industry Advisory Council for stakeholder engagementchemindia.chemicals
Future Scope:
- Software development and IT services expansion
- E-governance solutions and digital transformation
- Tech support for pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries
- Remote work opportunities leveraging scenic locations
5. Biotechnology Sector
Policy Framework: Dedicated Biotechnology Policy 2014 promoting bio-industrial developmentemerginghimachal.hp+2
- Research Infrastructure: CSIR-Institute of Himalayan Bioresource Technology, Palampuraspopharma
- Biotechnology Parks: Planned at Aduwal, Nalagarh in Solan districtplanning.hp+1
Applications:
- Herbal and medicinal plant processing
- Agricultural biotechnology for crop improvement
- Pharmaceutical biotechnology integration
- Environmental biotechnology solutions
6. Tourism and Hospitality
Economic Impact: Contributes 7% to state GDP with HPTDC turnover exceeding ₹100 crorehpsidc
- Tourist Arrivals: 181.24 lakh visitors annuallykhushru
- Policy Support: Himachal Pradesh Tourism Policy 2019 for sustainable developmenthpsidc
Emerging Trends:
- Eco-tourism development with 77 new sites generating ₹200 crore in 5 yearskhushru
- Adventure tourism expansion
- Wellness and spiritual tourism
- Digital tourism platforms and virtual experiences
Key Enabling Factors
1. Government Policies and Incentives
Industrial Investment Policy 2019 offers comprehensive incentives:himachalpr+1
- Capital subsidies up to 80% of fixed capital investment
- Land concessions: 50% for developed areas, 75% for tribal areas
- SGST reimbursement for 7 years
- Transportation cost reimbursement at 5% of annual income
Special Incentives:
- 70% employment reservation for locals
- Tax holidays and entry tax exemptions
- Anchor enterprise benefits for investments above ₹200 crorehimachalpr
2. Infrastructure Development
Transportation: Improved road connectivity through PMGSY, enhanced airports and railwaysemerginghimachal.hp
- Power Supply: Abundant and cheap electricity availability
- Industrial Areas: Well-developed industrial parks with modern facilitieskhushru+1
- Skill Development: Himachal Pradesh Skill Development Corporation initiativesemerginghimachal.hp
3. Strategic Location
- Proximity to major northern markets (Delhi, Punjab, Haryana)
- Access to raw materials and transportation networks
- Gateway to international markets through northern corridors
Emerging Opportunities
1. Mineral-based Industries
Resources Available:investindia+2
- Limestone (supporting cement industry)
- Rock salt (only state in India mining rock salt)
- Slate, marble, granite
- Gypsum, quartzite, and semi-precious stones
Development Potential:
- Modern mining techniques and mechanization
- Value-added mineral products
- Export-oriented mineral processing
2. Textile and Handicrafts
Traditional Strengths: Kullu shawls, Chamba rumal, woolen productscii
- Employment: 17,657 persons engaged in textile manufacturing (2022)managementjournal
- Government Support: PM MITRA Parks Scheme and PLI Scheme focusfoodprocessingindia
Modernization Scope:
- Integration of modern technology with traditional crafts
- Export market expansion
- Sustainable and eco-friendly textile production
Challenges and Solutions
1. Infrastructure Constraints
Challenge: Mountainous terrain limiting large-scale development
Solutions:
- Development of specialized hill-friendly industrial designs
- Improved connectivity through tunnel projects and modern transportation
- Distributed manufacturing models suitable for hilly terrain
2. Environmental Sustainability
Challenge: Balancing industrial growth with ecological preservation
Solutions:
- Mandatory environmental impact assessments
- Promotion of green technologies and clean manufacturing
- Strict pollution control measures and monitoring
3. Skilled Manpower
Challenge: Limited availability of specialized technical workforce
Solutions:
- Enhanced skill development programs
- Industry-academia partnerships
- Retention strategies for educated youth
Future Projections and Targets
Short-term Goals (2025-2027)
- Achieve Green Energy State status by 2026prsindia+1
- Complete Medical Devices Park development
- Expand pharmaceutical exports by 25%
- Establish 100 Green Panchayats with solar projectsprsindia
Medium-term Vision (2027-2030)
- Double renewable energy capacity to 20,000 MW
- Establish biotechnology as a major industrial sector
- Develop IT and software services significantly
- Achieve ₹500 crore food processing industry value
Long-term Aspirations (2030-2035)
- Become a major industrial hub in North India
- Achieve carbon neutrality in industrial operations
- Establish global leadership in sustainable mountain industrialization
- Create 500,000 additional industrial jobs
Investment Opportunities
High-Priority Sectors
- Renewable Energy Projects: Solar, hydro, and pump storage
- Pharmaceutical Manufacturing: APIs, biosimilars, medical devices
- Food Processing Units: Value addition, organic processing
- Biotechnology Ventures: Herbal processing, agricultural biotech
- IT and Software Development: Remote services, digital solutions
Government Support Mechanisms
- Single-window clearance system
- Industry Advisory Council guidance
- Public-private partnership models
- International collaboration facilitation
Employment Generation Potential
The state government has already provided 31,000 government sector jobs in the last two years. Future industrialization is projected to create:himachalservices
- Direct Employment: 200,000-300,000 jobs across all sectors
- Indirect Employment: 400,000-500,000 jobs in ancillary industries
- Skilled Employment: Focus on technical and managerial positions
- Women’s Participation: 700 female apprentices in power sector aloneindianjournalofeconomicsandresearch
Conclusion
Himachal Pradesh presents exceptional scope for future industrialization, combining natural advantages with progressive policies and strategic vision. The state’s commitment to sustainable development, coupled with its strong performance in pharmaceuticals, renewable energy, and food processing, positions it as a model for mountain state industrialization. Success will depend on maintaining the balance between economic growth and environmental conservation while leveraging the state’s unique geographical and cultural advantages.
The comprehensive policy framework, infrastructure development initiatives, and focus on emerging technologies create a conducive environment for investors and entrepreneurs. With continued government support and strategic investments, Himachal Pradesh is poised to become a significant industrial contributor to India’s economy while maintaining its ecological integrity and cultural heritage.
Here’s your SEO-friendly rewrite of the content on Major Impediments and Solutions for Industrial Growth in Himachal Pradesh, keeping it keyword-rich, easy to read, and optimized for search engines while retaining all original details.
Major Impediments and Strategic Solutions for Industrial Growth in Himachal Pradesh
Overview
Himachal Pradesh has emerged as a fast-growing industrial hub in North India, especially in pharmaceutical manufacturing, food processing, and light engineering. However, the state still faces significant infrastructure, geographic, policy, and human resource challenges that hinder its full industrial potential. This article explores the top 15 challenges and practical solutions for sustainable industrial growth.
15 Major Impediments to Industrial Growth in Himachal Pradesh
1. Infrastructure Challenges
- Lack of Railway Connectivity – Most industrial clusters, like Baddi-Barotiwala-Nalagarh, lack direct rail access, increasing logistics costs and limiting raw material transport.
- Poor Road Infrastructure – Frequent landslides, narrow mountain roads, and poor maintenance disrupt supply chains.
- Inadequate Power Supply – Despite hydro potential, industries face power cuts and high tariffs. Withdrawal of concessional rates has reduced competitiveness.
- Limited Industrial Land – Mountainous terrain limits flat land availability; major estates are already saturated.
2. Geographic & Logistical Constraints
- High Transportation Costs – Mountain transport is 2–3 times more expensive; truck cartels increase freight rates.
- Distance from Ports and Markets – Landlocked location raises export costs; goods travel long distances to ports in Gujarat or Maharashtra.
- Difficult Topography – Steep terrain limits heavy industry and large-scale operations.
- Seasonal Accessibility – Remote areas face disruptions during monsoons and winters.
3. Human Resource Deficiencies
- Skilled Labor Shortage – Lack of industry-ready technical workers; industries import manpower.
- Migrant Labor Dependency – 70–80% of workers come from outside, leading to instability.
- Managerial Talent Scarcity – Many qualified professionals migrate to metro cities.
4. Financial & Economic Barriers
- High Raw Material Costs – Distance from suppliers and small-scale procurement increase prices.
- Limited Credit Access – Poor banking penetration and cautious lending hurt SME growth.
- High Operational Costs – Setting up industries costs 15–20% more than in plains.
5. Policy & Regulatory Issues
- Complex Clearance Procedures – Multiple approvals and bureaucratic delays despite a single-window system.
15 Strategic Solutions for Industrial Growth
A. Infrastructure Development
- Railway Network Expansion – Connect major hubs to the Baddi-Chandigarh-Delhi rail corridor.
- All-Weather Road Infrastructure – Build tunnels, bridges, and predictive road maintenance systems.
- Dedicated Industrial Power Grid – Create separate supply lines and promote renewable energy.
- Integrated Industrial Parks – Sector-specific clusters with ready infrastructure.
B. Transportation & Connectivity
- Multimodal Logistics Hubs – Combine road, rail, and air cargo facilities.
- Freight Corridors & Warehousing – Modern warehouses and container depots at key points.
- Alternative Transport – Cable cars and helicopter services for difficult terrain.
C. Human Resource Development
- Technical Education Enhancement – Industry-specific universities and R&D centers.
- Industry-Academia Partnerships – Internships, joint research, and curriculum upgrades.
- Local Skill Development – Vocational programs for youth in demand sectors.
D. Financial Support
- Industrial Development Banking – Concessional loans for SMEs and startups.
- Raw Material Support Systems – Bulk procurement cooperatives.
- Venture Capital Ecosystem – State-backed funds for innovation.
E. Policy & Governance Reforms
- Effective Single-Window System – Fully digital, time-bound approvals.
- Digital Governance – Real-time monitoring and transparent processes.
Implementation Timeline
- Immediate (0–2 years): Rail connectivity, power upgrades, skill training, digital clearance system.
- Medium Term (2–5 years): Industrial parks, logistics infrastructure, concessional finance.
- Long Term (5–10 years): World-class technical institutes, export-oriented clusters, advanced manufacturing hubs.
Conclusion
Industrial growth in Himachal Pradesh is constrained by geography, infrastructure gaps, and policy delays, but targeted reforms can unlock its potential. By investing in connectivity, industrial parks, skill development, and digital governance, Himachal Pradesh can position itself as a competitive manufacturing and export hub in India’s northern region.
SEO Keywords Used: industrial growth in Himachal Pradesh, industrial policy Himachal, challenges for industries in Himachal, solutions for Himachal industrialization, Baddi-Barotiwala industrial hub, Himachal manufacturing sector, industrial infrastructure Himachal Pradesh.
If you want, I can now convert this into a keyword-optimized comparison table of challenges vs solutions so that it ranks better for competitive and informational queries. That would make it even more effective for both Google SEO and exam preparation.
Major Impediments and Solutions for Industrial Growth in Himachal Pradesh
Overview
Despite Himachal Pradesh’s remarkable transformation into a significant industrial hub, particularly in pharmaceuticals and manufacturing, the state continues to face substantial challenges that impede its industrial growth potential.himachalpradesh.pscnotes+2
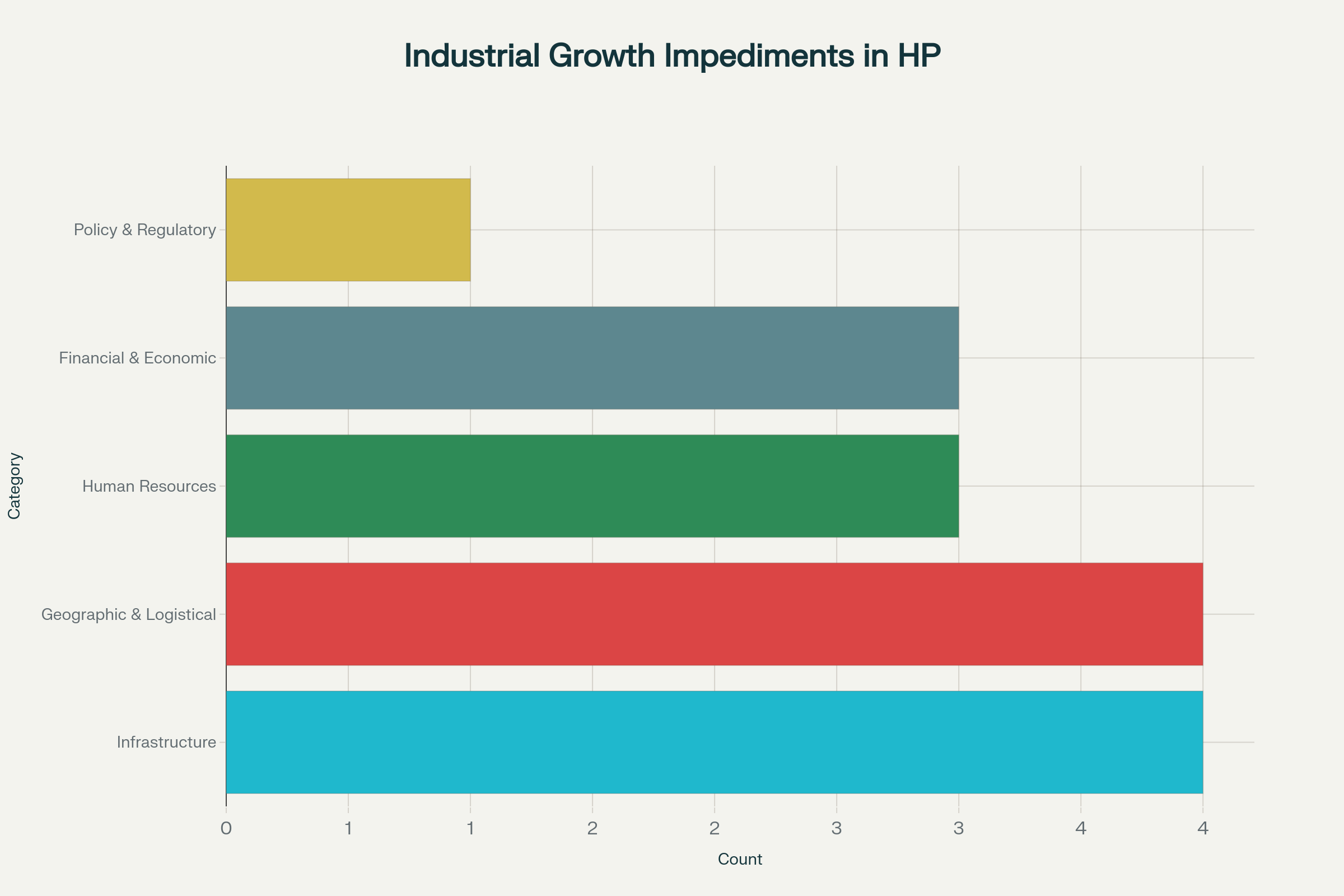
Distribution of industrial growth impediments by category in Himachal Pradesh
15 Major Impediments to Industrial Growth
Infrastructure Challenges (4 impediments)
1. Lack of Railway Connectivity – Most industrial areas lack direct rail access, forcing complete dependence on road transport. This increases logistics costs significantly and limits raw material procurement options.timesofindia.indiatimes+1
2. Poor Road Infrastructure – Frequent landslides, narrow mountain roads, and inadequate maintenance disrupt supply chains. The damaged road network acts as a severe bottleneck in transportation of goods.hpgeneralstudies+1
3. Inadequate Power Supply – Despite hydroelectric potential, industries face power outages and high electricity tariffs. The recent withdrawal of concessional power rates has made HP less competitive with neighboring states.timesofindia.indiatimes+1
4. Limited Industrial Land – Mountainous terrain restricts availability of flat land suitable for industrial development. Existing industrial estates are saturated, particularly in successful clusters like Baddi-Barotiwala-Nalagarh.emerginghimachal.hp+1
Geographic & Logistical Constraints (4 impediments)
5. High Transportation Costs – Mountainous terrain makes transportation 2-3 times more expensive than plain areas. Truck unions often act as cartels, charging exorbitant rates.timesofindia.indiatimes+1
6. Distance from Ports and Markets – Landlocked location increases export costs significantly. Products must travel long distances to reach ports in Gujarat or Maharashtra.managementjournal
7. Difficult Topography – Steep terrain restricts large-scale industrial operations and heavy machinery installation. This limits economies of scale and heavy industry development.hpgeneralstudies+1
8. Seasonal Accessibility – Remote areas become inaccessible during monsoons and winters, causing production disruptions and supply chain interruptions.logisticsinsider
Human Resource Deficiencies (3 impediments)
9. Skilled Labor Shortage – Limited availability of technically skilled workers forces industries to import labor. Local technical education doesn’t align with industry requirements.link.springer+1
10. Migrant Labor Dependency – About 70-80% of industrial workforce comes from other states, creating instability and higher labor costs during festivals and emergencies.hpgeneralstudies
11. Managerial Talent Scarcity – Lack of experienced management professionals limits industrial growth. Most local graduates migrate to metros for better opportunities.link.springer
Financial & Economic Barriers (3 impediments)
12. High Raw Material Costs – Distance from source regions and transportation difficulties increase input costs. Limited bulk procurement options further inflate prices.managementjournal
13. Limited Credit Access – Insufficient banking infrastructure and risk-averse lending practices restrict industrial financing. Small and medium enterprises particularly struggle with credit access.phdcci
14. High Operational Costs – Establishment and running costs are 15-20% higher than plain areas. This affects competitiveness in national and international markets.timesofindia.indiatimes+1
Policy & Regulatory Issues (1 impediment)
15. Complex Clearance Procedures – Despite single-window systems, multiple approvals cause delays. Bureaucratic lethargy in implementing policy promises creates investor uncertainty.timesofindia.indiatimes+1
15 Strategic Solutions for Industrial Growth
Infrastructure Development (4 solutions)
1. Railway Network Expansion – Develop dedicated freight rail links connecting major industrial clusters to national network. Priority should be given to Baddi-Chandigarh-Delhi corridor.timesofindia.indiatimes
2. All-Weather Road Infrastructure – Build tunnels and bridges to ensure year-round connectivity. Implement modern road maintenance systems using technology for predictive repairs.hpgeneralstudies
3. Dedicated Industrial Power Grid – Create separate power distribution networks for industrial zones. Establish captive power plants and renewable energy projects to ensure reliable supply.chemindia.chemicals
4. Integrated Industrial Parks – Develop plug-and-play industrial facilities with pre-approved infrastructure. Focus on creating sector-specific clusters with shared facilities.indiafilings+1
Transportation & Connectivity (3 solutions)
5. Multimodal Transportation Hubs – Establish integrated logistics centers combining road, rail, and air connectivity. Develop inland container depots for efficient cargo handling.phdcci
6. Freight Corridors and Logistics Parks – Create dedicated freight movement channels. Establish modern warehousing and distribution centers at strategic locations.chemindia.chemicals
7. Alternative Transport Solutions – Develop helicopter services and cable car systems for difficult terrain areas. This can ensure connectivity to remote industrial locations.hpgeneralstudies
Human Resource Development (3 solutions)
8. Technical Education Enhancement – Establish specialized technical universities aligned with industry needs. Create Centers of Excellence in emerging technologies.indiafilings+1
9. Industry-Academia Partnerships – Develop mandatory internship programs and industry-sponsored research. Ensure curriculum design involves industry stakeholders directly.phdcci
10. Local Skill Development – Implement comprehensive vocational training programs targeting local youth. Focus on creating skilled workforce in high-demand industrial sectors.himachal
Financial Support Mechanisms (3 solutions)
11. Specialized Industrial Banking – Create dedicated industrial development banks offering concessional credit. Implement risk-sharing mechanisms to encourage lending to SMEs.phdcci
12. Raw Material Support Systems – Establish bulk procurement cooperatives and material banks. Negotiate group contracts for common raw materials across industries.chemindia.chemicals
13. Venture Capital Ecosystem – Create state-sponsored venture capital funds for startups and innovation. Encourage private investment in emerging technology sectors.indiafilings
Policy & Governance Reforms (2 solutions)
14. Effective Single-Window System – Implement truly integrated online clearance portals. Establish time-bound approvals with automatic clearance for delays.timesofindia.indiatimes+1
15. Digital Governance Framework – Digitize all industrial approvals and monitoring systems. Create transparent, accountable processes with real-time tracking capabilities.indiafilings
Implementation Priority Matrix
Immediate Priority (0-2 years):
- Railway connectivity projects
- Single-window clearance digitization
- Power infrastructure development
- Skill development programs
Medium-term Priority (2-5 years):
- Integrated industrial parks
- Logistics infrastructure
- Financial support mechanisms
- Alternative transport systems
Long-term Priority (5-10 years):
- Technical education institutions
- Research and development centers
- Advanced manufacturing clusters
- Export infrastructure development
Conclusion
Himachal Pradesh’s industrial growth impediments are primarily structural, rooted in its geographic challenges and infrastructure deficits. However, with systematic implementation of these solutions, the state can overcome these constraints and realize its full industrial potential. The key lies in coordinated action across infrastructure development, human resource enhancement, and policy reforms, leveraging the state’s natural advantages while mitigating its inherent challenges.hpgeneralstudies+2
Significant achievements in the field of industrialisation
- Promotion of MSME
- e.g., 80,000 enterprises registered on Udyam portal
- Hydropower Sector
- 4000 MW of installed capacity
- Pharmaceutical Industry
- Contributes 35% of India’s demand
- Agro-Based Industries
- 2nd Rank in Apple and Almond Production
- Tourism-linked IndustryEase of Doing Business Index
- Single window platform in Himachal
- Employment
- PCI increased
- Manufacturing sector growth rate
- BBN recognised as India’s largest pharmaceutical cluster
- HP Best State in Food Processing 2024
- Targets: 100% solar then renewable by 2030
Types of Protectionist Measures
- Tariffs
- Ad valorem import tax
- Quotas and Embargoes
- Quantitative limits or outright bans on imports
- Non-Tariff Barriers
- Subsidies
- Public procurement policies
- Licensing
- Technical standards
- Sanitary/Phyto-sanitary requirements
- Anti-dumping/Countervailing duties
Macro-Economic Effects
- Decline in trade volume
- Higher consumer prices and inflation
- Protected industries → ↓ Competitive pressure → Inefficiency & ↓ Innovation
- Trade policy spillovers and retaliation
- (Trade wars → Uncertainty → ↓ Investment)
- Exchange rate crisis
- Supply chain and value chain reconfiguration
- (↑ Friend-shoring) → Accelerates regionalism
- Institutional & Legal implications → WTO conflict
World Trade
- Less resilient
- More unequal
- More conflict-prone
